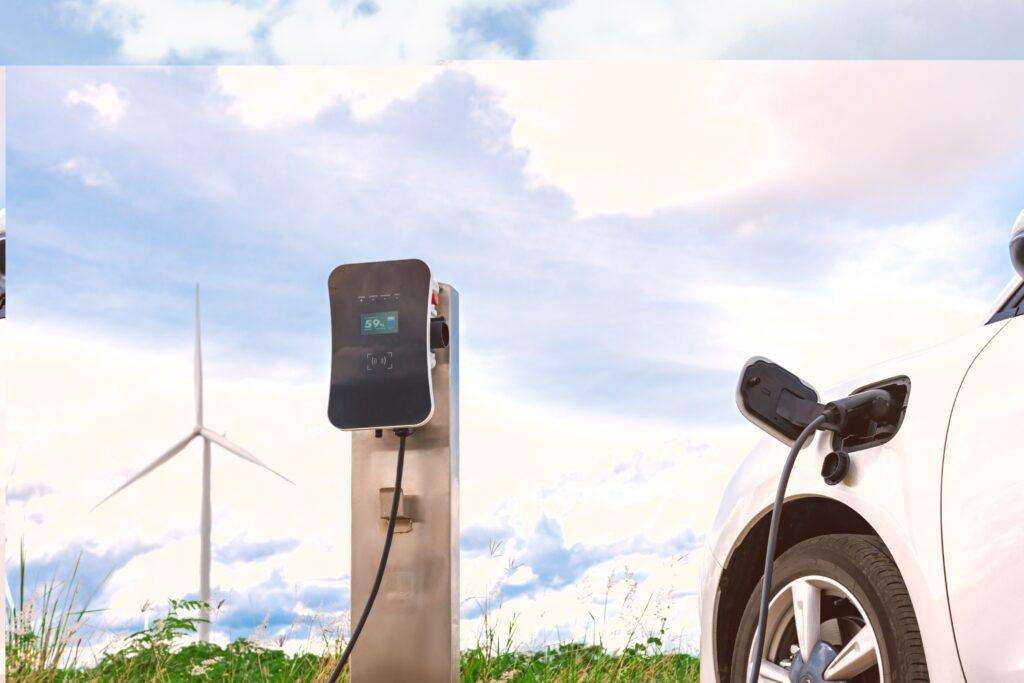
The transition to electric vehicles in commercial fleets is a crucial part of the global strategy for reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainability. However, the widespread adoption of electric vehicles in commercial fleets, especially in areas far from urban centres or in regions with limited basic infrastructure, entails considerable logistical obstacles.
Creating a suitable charging infrastructure in these remote areas is hampered by several factors, including the restricted access to reliable energy sources or the lack of connections established with the main electrical grid. What’s more, the specific geographical nature of these areas can further complicate the installation and maintenance of charging stations, increasing costs and implementation times.
To overcome these challenges, the development and implementation of innovative solutions that can adapt to the specific limitations of these areas is essential. These solutions include the use of advanced energy storage technologies, such as high-capacity batteries that can charge during low demand periods and supply electricity for vehicle charging during peak usage.
Likewise, the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines into charging infrastructure can provide a sustainable energy source and reduce dependence on the electrical grid. In this regard, the collaboration between companies, governments and other organisations is crucial to addressing these challenges which are both logistical and financial, facilitating the creation of a charging ecosystem which is accessible, efficient and sustainable.
Key charging challenges in remote areas
- Limited access to the electrical grid: in remote areas, the connection to the electrical grid may be weak or non-existent, making it difficult to install conventional charging stations.
- High infrastructure costs: extending electrical infrastructure to remote locations can be prohibitively expensive, both in terms of construction and maintenance.
- Geographic and climatic considerations: factors such as difficult terrain, extreme weather conditions, and distance to urban centres can further complicate the installation and operation of charging infrastructure.
Solution strategies
- On-site renewable energy or on-site PPA: one viable solution is the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, to generate electricity on-site. This not only reduces dependence on the electrical grid but it also ensures a sustainable, low-cost energy source. Combining these sources with energy storage systems, such as batteries, can ensure constant charging even under variable conditions.
- Mobile charging solutions: mobile charging, where charging units are transported to the vehicle rather than being fixed, affords great flexibility. It is particularly useful in areas when installing permanent infrastructure is not feasible. Mobile charging units can be powered by conventional generators or renewable sources and relocated as necessary.
- High efficiency charging technology: investing in high-efficiency fast charging technology can significantly reduce loading times, making operations in remote areas more feasible. Although this requires a larger initial investment, the long-term savings in operating time may justify the expense.
- Strategic planning and site analysis: performing detailed site and energy demand analyses can help identify the most strategic locations for the installation of charging points. This includes assessing accessibility, geographic and climatic conditions and proximity to existing transportation routes.
- Public-private partnerships: forging alliances between companies, local governments and energy providers can be key to overcoming logistical and financial challenges. These partnerships can facilitate investment in charging infrastructure and get the most out of innovative financing and operating models.
- Incentives and subsidies: taking advantage of government incentives and subsidies for green infrastructure development can help mitigate installation and operating costs in remote areas.
Meeting the logistical challenges of deploying charging infrastructure for electric vehicle fleets in remote areas requires a multifaceted approach, which combines technological innovation, collaboration and strategic planning. Through the adoption of renewable energies, mobile charging solutions, and making the most of incentives, businesses can overcome these obstacles.
Implementing effective strategies will not only facilitate the transition to electric vehicle fleets in remote areas, but it will also contribute to global sustainability and emissions reduction goals.